Charge air conditioning gas How to do it?
Gas charge, when is it elemental?
A charge or gas refill in our air conditioning does not have to be elementary NEVERunless we have a gas leak in our refrigeration circuit, these gas leaks have the possibility of occurring due to numerous causes that we already address in another article and before any recharging the leak should be located and repairedthat’s why we should first detect that the failure of our air conditioner comes precisely from a lack of refrigerant and once the problem is clarified, look for and fix this leak before doing any gas loading.
If you have concerns about whether your air conditioner lacks gas or if what is necessary for you is to locate this leak, these two articles will help you know if there is a lack of gas or not and if so, try to locate the presence of this gas leak.
Essential tools for a gas load
If we already know that our machine is out of gas, we sought the escape and repaired it, at this moment is the moment to do a gas refill to give life to our air conditioner again, for this reason and more than anything to do it right, we will need numerous typical utilities of a refrigerator:
- vacuum pump
- manometer
- scale
- Refrigerant gas bottle used by our air conditioner




Steps to continue to perform a gas charge correctly
Connect the manometers

The first thing we will have to do is connect the hoses of the pressure gauges to the howitzer of our air conditioner. There are machines that have two shell sockets (high and low pressure), on the other hand there are other machines that only have one socket, the latter tend to be generally the split type entities and the most common in some homes. This shell outlet will be high pressure when we have the machine running in heat pump mode and low pressure when it is running in cold mode.
If your set has two howitzer sockets, we will connect the red hose to the high pressure socket and the blue hose to the low pressure socket.
If your set only has one shell socket, in relation to the season of the year we will have to connect one or the other, the blue one if we plan to turn on the machine in cold mode and the red one if we plan to turn it on in pump mode heat since this shell as we said it will become high or low pressure in relation to whether we choose one method or another of development.
Realize the void
Once the pressure gauge is connected to the shell socket(s), we will connect the yellow hose (the one in the middle) to the socket of the vacuum pump, since before making any gas load it is advisable and essential to make an optimum empty in the refrigeration circuit.
Making a vacuum in the refrigeration circuit of the machine is required for numerous reasons:
- Removes the air in the refrigeration circuit.
- Removes moisture that could have entered the refrigeration circuit.
- It helps to do the gas charge, as by getting the air from inside the circuit this will help the refrigerant gas to enter much faster.
Once that’s done, we’ll turn on the vacuum pump and let it do the job for “a good while,” but what measure of time is “a good while”? Since it is dependent, it depends on the type of installation, the size of the machine and the distance of the pipes, it depends on the capacity of the vacuum pump and in addition it depends on the type of escape and the time required by the machine without gas, however if in doubt it is preferable to stay extensive as strong as short for little.
Generally if a machine has not lost 100% gas it is impossible for air or moisture to enter the circuit, since any small proportion of gas remaining in the refrigeration circuit will be sufficient to maintain its pressure higher than the ambient pressure and then avoid the entry of air.
Load up on gas
Once the vacuum is made, it’s time to load with gas. Since there are currently and are used several types of refrigerant gases (R-22, R-407, R-410, R-424, ISCEON, etc.), some azeotropic and others not, we will gas charge in the manner valid for any class of gas: this way it will be in a liquid state and by weight.
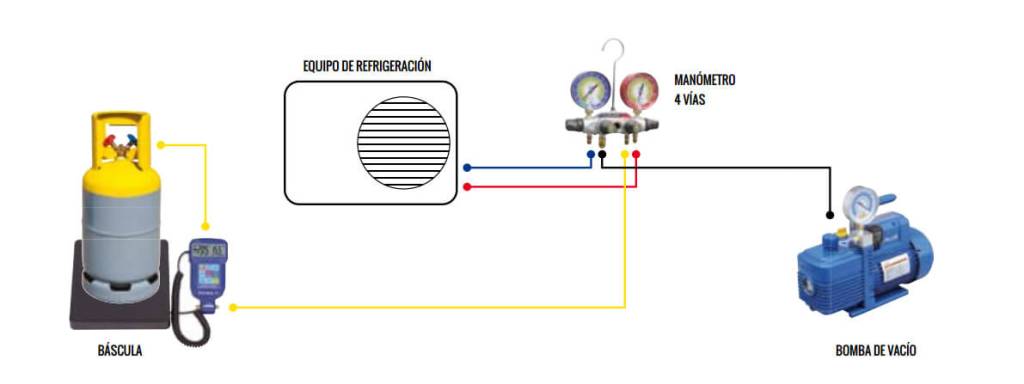
To do this load of refrigerant we will need the scale and the bottle of the corresponding refrigerant, since to carry it out in the preferable way it is necessary to carry out as we said by weight and with the refrigerant in a liquid state.
Before placing the bottle on the scale, there is a consideration with the gas bottle.
Place the bottle on the scale precisely
There are several types of bottles according to developers, some have two independent outlets for gas and liquid, others only have an unsheathed or sheathed socket. This is considerable to own clear since of this it will depend on whether or not we have to offer return to the bottle.
The first thing we have to do is place the bottle of refrigerant gas on top of the scale and connect the yellow socket that we had connected to the vacuum pump to its socket, once this is done we should take the scale so that this is set to 0.000 kg., since we will monitor the load and the proportion of gas that enters as the bottle becomes thinner.
Having everything mentioned nearby, we will have to open the bottle and then open the manometer key to offer passage to the gas and that refrigerant begins to flow into our air conditioner. Charging time will depend on bottle pressure, refrigerant ratio, temperature, etc. five to ten minutes would be plenty unless the pressure of the two (bottle and machine) is balanced and does not let us put more gas in, in these cases it will be essential start the machine to lower the pressure and suck up the gas.
Remember that the gas charge with our walking air conditioner it will only be viable for low pressureso if we have a set that has two shells (high and low) we will only open in this situation to follow the charge of refrigerant the low pressure one and if our unit only has one shell outlet, anyway we will have to take the unit in cold or dry mode since in a hot way the pressure would go up a lot and we would be realizing the opposite effect (passing gas from the machine to the bottle).
Once we observe on our scale that the same proportion of gas required by our set has been subtracted, we will close the bottle, manometers and give the work as completed.
The best way to gas an air conditioner is to do it by weight and in a liquid state
When it costs a load of air conditioning gas
Another normal doubt is the price that has a gas load and it is very logical since it is not dependent on only one aspect nor is it something that is standardized. The reasons for appreciating the value of a load of gas are numerous and we present them here briefly:
- Type of fluorinated gas: There are a multitude of fluorinated gases or refrigerant gases that are used in air conditioning units, the most common are R410, R407, R22 and their substitutes such as RS44 / R424A (there are several others).
- Tax on fluorinated gases: In relation to the country where you reside, the state can tax this class of gases with notable taxes, in the situation of Spain these taxes depend on the global warming potential of each type of gas. Some gases pay more taxes and others less.
- Amount of gas: Not only is the type of gas and its particular tax considerable, we also have to take into account the proportion of gas that our machine transports. In most cases, split air conditioning units of 2,000 or 3,000 fridges tend to require over one kilogram of gas, whereas ducted units or centralized domestic air conditioning units tend to require between three and five kilograms.
- Installer or technician company margin: This point is the only variable in the equation since the proportion of gas we require is suggested by our machine to its technical properties, the tax is something that goes by law and then it is a fixed amount, but the margin you want us to add to the technician for his work, handling or costs will be what in the end accurately determines the value of our gas load.
How to understand the amount and type of gas your air conditioner uses
As you can see, in order to carry out an accurate estimate of how much a load of gas can cost, we require a lot of data that we have the ability to know in a simple way seeing the technical properties of our machine and of course asking the repair company how much it costs or will charge us for each kg of gas. The price a technician usually charges for gas can be between €20 and €60 per kilogram + taxes + VAT.



Leave a Comment